recruitCTF2024
Lời giải cho các challenge crypto mình ra trong recruitCTF 2024 của blackpinker
Baby Pad
Challenge
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import os
with open('./FLAG.txt', 'rb') as f:
flag = f.readline()
def pad(message):
l = -len(message) % 16
if l == 0:
l = 16
return message + bytes([l]) * l
def check_pad(message):
l = message[-1]
if not (l >= 1 and l <= 16):
return False
return message[-l:] == bytes([l] * l)
key = os.urandom(16)
iv = os.urandom(16)
def encrypt(message, iv):
cipher = AES.new(key = key, iv = iv, mode = AES.MODE_CBC)
return cipher.encrypt(message)
def decrypt(message, iv):
cipher = AES.new(key = key, iv = iv, mode = AES.MODE_CBC)
return cipher.decrypt(message)
ct = iv + encrypt(pad(flag), iv)
print(f"enc = {ct.hex()}")
while True:
print('1. Send me a message!')
print('2. 1 is your only choice actually')
choice = input("Your choice: ")
if choice == '1':
ciphertext = bytes.fromhex(input())
iv = bytes.fromhex(input())
message = decrypt(ciphertext, iv)
if not check_pad(message):
print("Can't read that")
else:
print("Message received!")
else:
print("Good bye")
exit()
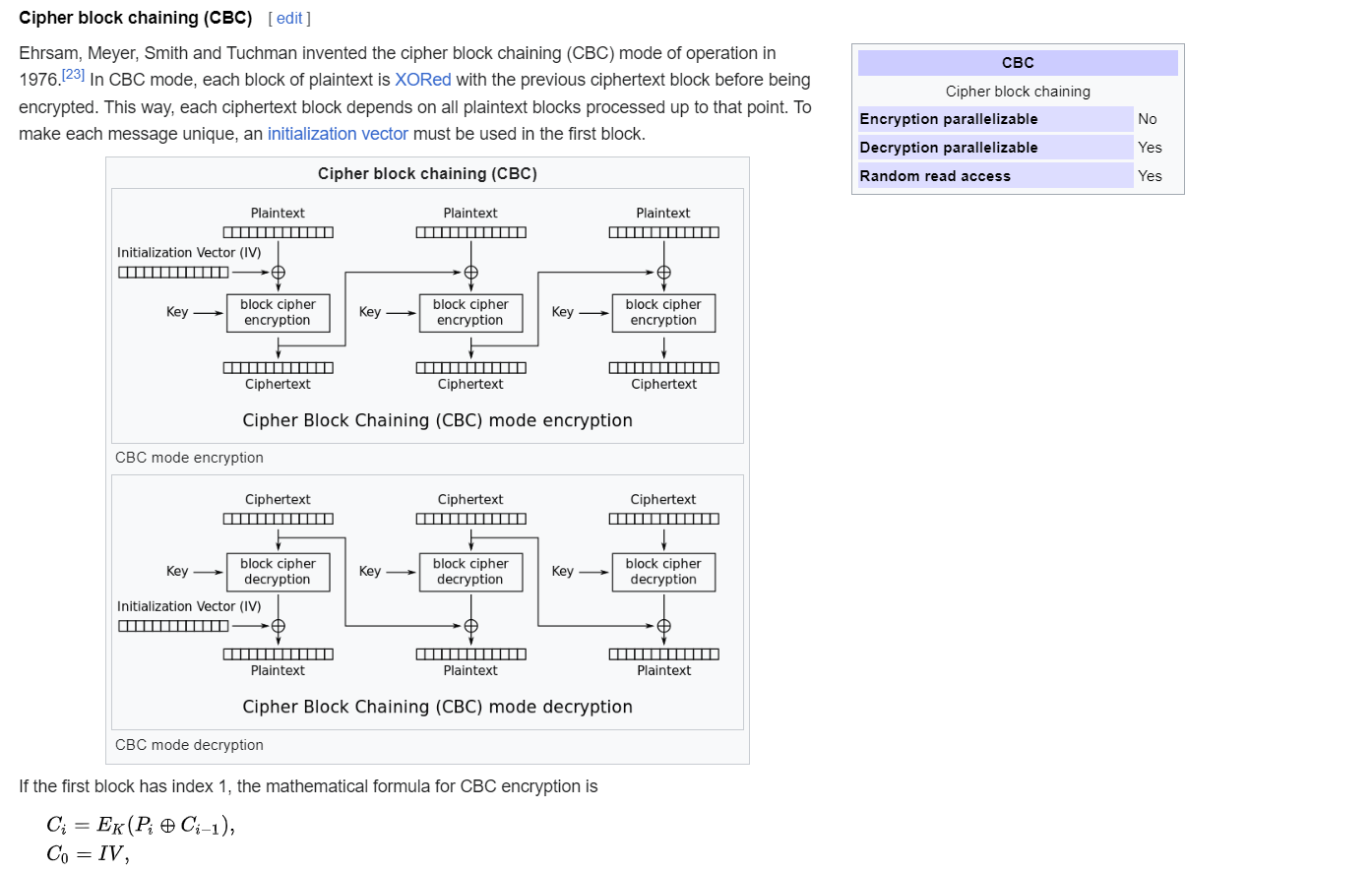
Server cho mình gửi iv và ciphertext lên và sử dụng AES-CBC để decrypt, sau đó check padding và nếu padding đúng thì print("Message received!") không thì print("Can't read that")
Solution
Đầu tiên mình đi check hàm pad của đề:
1
2
3
4
5
def pad(message):
l = -len(message) % 16
if l == 0:
l = 16
return message + bytes([l]) * l
Giả sử như mình gọi pad(a) với len(a) = 15 thì mình sẽ có pad(a) = a + b'\x01', len(a) = 14 thì pad(a) = a + b'\x02' * 2, …
Tiếp theo mình cùng nhìn cách hoạt động của AES-CBC:
Thay vì nhìn từng block thì mình sẽ nhìn từng byte
Mình sẽ tập trung ở phần decrypt, xét 2 block ciphertext đầu tiên:
Block thứ nhất có các bytes: $C_0, C_1, \dots, C_7$. Block thứ hai có các bytes: $C_8, C_9, \dots, C_{15}$
Nhìn hình thì mình có:
$P_{15} = D(C_{15}) \oplus C_7$, $P_{14} = D(C_{14}) \oplus C_6$, $\dots$
Mục tiêu của mình sẽ là tìm được hết tất cả $P_i$
Mình có thể lợi dụng việc server cho mình biết padding đúng hay sai như sau:
Mình sẽ tìm $C_7’$ sao cho $P_{15}’ = D(C_{15}) \oplus C_7’ = 1$, lúc này server sẽ trả về print("Message received!") do padding đúng, các trường hợp $C \neq C_7’$ sẽ trả về print("Can't read that").
Từ đây mình có thể tìm lại được $D(C_{15}) = 1 \oplus C_7’$ $\Rightarrow$ tìm lại được $P_{15}$
Tiếp theo thì mình sẽ tìm $P_{14}$ như sau:
Đặt $C_7’ = D(C_{15}) \oplus 2$ rồi tiếp tục tìm $C_6’$ sao cho $P_{14}’ = D(C_{14}) \oplus C_6’ = 2$
Khi này decrypt ra thì block sẽ trông thế này:
$P_7P_8\dots P_{14}’P_{15}’ = P_7P_8\dots \text{x02x02}$ trả về padding hợp lệ và print("Message received!")
Từ đó mình biết $D(C_{14}) = 2 \oplus C_6’$ $\Rightarrow$ tìm lại được $P_{14}$
Mình lặp lại quá trình này đến khi tìm hết 1 block rồi tiếp tục sang block tiếp theo đến khi có được toàn bộ plaintext ban đầu.
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from pwn import *
LOCAL = False
if LOCAL: io = process(["python3", "chall.py"])
else: io = remote('blackpinker.rocks', 30276)
ct = io.recvline().decode().split(' = ')[-1].strip()
ct = bytes.fromhex(ct)
block = [ct[i:(i + 16)] for i in range(0, len(ct), 16)]
from pwn import xor
def solve_block(block, iv):
known = b''
while len(known) != 16:
prefix = bytes(16 - len(known) - 1)
postfix = bytes([a ^ (len(known) + 1) for a in known])
for x in range(0, 256):
forged_iv = prefix + bytes([x]) + postfix
io.sendlineafter("Your choice: ", '1')
io.sendline(block.hex())
io.sendline(forged_iv.hex())
respone = io.recvline().decode().strip()
if respone == "Message received!":
print(len(known))
known = bytes([x ^ (len(known) + 1)]) + known
break
return xor(known, iv)
flag = b''
for i in range(len(block) - 1, 0, -1):
cur = block[i]
iv = block[i - 1]
flag = solve_block(cur, iv) + flag
print(flag)
print(flag)
# BPCTF{Just_a_simple_padding_oracle_attack_to_warm_up}
Baby RSA 1
Challenge
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from Crypto.PublicKey import RSA
with open('./FLAG.txt', 'rb') as f:
flag = f.read()
def gen_key():
key = RSA.generate(2024)
public_key = (key.n, key.e)
private_key = (key.p, key.q, key.d)
return public_key, private_key
def decrypt_data(c, private_key, q_inv):
"""
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RSA_(cryptosystem)#Using_the_Chinese_remainder_algorithm
"""
p, q, d = private_key[0], private_key[1], private_key[2]
dp, dq = d % (p - 1), d % (q - 1)
m1 = pow(c, dp, p)
m2 = pow(c, dq, q)
h = q_inv * (m1 - m2) % p
m = m2 + h * q % (p * q)
return long_to_bytes(m)
def get_encrypted_flag(flag, public_key):
n, e = public_key[0], public_key[1]
flag = bytes_to_long(flag)
flag_enc = pow(flag, e, n)
return long_to_bytes(flag_enc)
border = '-' * 69
public_key, private_key = gen_key()
flag_enc = get_encrypted_flag(flag, public_key).hex()
c = ''
while True:
print(border)
print('1. Decrypt data')
print('2. Get public key')
print('3. Get encrypted flag')
print(border)
choice = input('Enter your choice: ')
if choice == '1':
if c == '':
c = input('Enter your ciphertext in hex string: ')
c = int(c, 16)
if c == int(flag_enc, 16):
print("No cheating")
exit()
num = int(input('Enter your magic number: '))
msg = decrypt_data(c, private_key, num).hex()
print(msg)
elif choice == '2':
print(f'n = {public_key[0]}')
print(f'e = {public_key[1]}')
elif choice == '3':
print(flag_enc)
else:
print('Bye')
exit()
Server cho mình decrypt một ciphertext bất kì sử dụng RSA-CRT và cho mình tùy ý chọn $q^{-1} \pmod {p}$
Solution
Cả hai bài RSA mình đều code ẩu nên thành ra có rất nhiều unintended solutions :( , mình sẽ nói sơ về cách của mình (sẽ add những cách khác khi rảnh).
Gửi 2 con magic number ta có:
$ h_1 \equiv q^{-1}_1(m1 - m2) \pmod{p}$ và $ h_2 \equiv q^{-1}_2(m1 - m2) \pmod{p}$
$ msg_1 \equiv m_2 + h_1q \pmod{n}$ và $ msg_2 \equiv m_2 + h_2q \pmod{n}$
$msg_1 - msg_2 = (h1 - h2)q$
Từ đây ta có thể lấy gcd với $n$ và tìm lại $q$ rồi decrypt ciphertext.
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
from pwn import *
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes as ltb, GCD
LOCAL = False
if LOCAL: io = process(["python3", "server.py"])
else: io = remote("blackpinker.rocks", 30541)
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your choice:', '2')
n = int(io.recvline().split(b' = ')[-1].decode())
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your choice:', '1')
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your ciphertext in hex string:', hex(2))
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your magic number:', '69')
t1 = int(io.recvline(), 16)
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your choice:', '1')
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your magic number:', '420')
t2 = int(io.recvline(), 16)
test = (t1 - t2) % n
q = GCD(test, n)
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your choice:', '3')
ct = int(io.recvline(), 16)
p = n // q
d = pow(65537, -1, n - p - q + 1)
flag = pow(ct, d, n)
print(ltb(flag))
# BPCTF{Thank_you_naul_for_finding_this_not_so_intended_solution}
io.interactive()
Another solution:
Baby RSA 2
Challenge
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from Crypto.PublicKey import RSA
with open('./FLAG.txt', 'rb') as f:
flag = f.read()
def gen_key():
key = RSA.generate(2024)
public_key = (key.n, key.e)
private_key = (key.p, key.q, key.d)
return public_key, private_key
def decrypt_data(c, private_key, q_inv):
"""
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RSA_(cryptosystem)#Using_the_Chinese_remainder_algorithm
"""
p, q, d = private_key[0], private_key[1], private_key[2]
dp, dq = d % (p - 1), d % (q - 1)
m1 = pow(c, dp, p)
m2 = pow(c, dq, q)
h = q_inv * (m1 - m2) % p
m = m2 + h * q % (p * q)
return long_to_bytes(m)
def get_encrypted_flag(flag, public_key):
n, e = public_key[0], public_key[1]
flag = bytes_to_long(flag)
flag_enc = pow(flag, e, n)
return long_to_bytes(flag_enc)
border = '-' * 69
public_key, private_key = gen_key()
flag_enc = get_encrypted_flag(flag, public_key).hex()
num = ''
while True:
print(border)
print('1. Decrypt data')
print('2. Get public key')
print('3. Get encrypted flag')
print(border)
choice = input('Enter your choice: ')
if choice == '1':
c = input('Enter your ciphertext in hex string: ')
c = int(c, 16)
if c == int(flag_enc, 16):
print("No cheating")
exit()
if num == '':
num = int(input('Enter your magic number: '))
try: assert num.bit_length() > 69 and num.bit_length() < 690
except AssertionError: print("Bye"); exit()
msg = decrypt_data(c, private_key, num).hex()
print(msg)
elif choice == '2':
print(f'n = {public_key[0]}')
print(f'e = {public_key[1]}')
elif choice == '3':
print(flag_enc)
else:
print('Bye')
exit()
Cũng như trên, mình sẽ nói cách giải intended (vì author code ẩu nên đẻ nhiều unintended).
Bài này khác bài 1 ở chỗ là lần này chúng ta được gửi nhiều c nhưng chỉ được gửi 1 q_inv
Solution
Để ý rằng khi m < q thì msg ta decrypt được sẽ đúng với ban đầu, không thì ngược lại. Vậy nên ta có thể binary search để tìm lại $q$.
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
from pwn import *
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes as ltb, GCD
LOCAL = False
if LOCAL: io = process(["python3", "server.py"])
else: io = remote("blackpinker.rocks", 30609)
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your choice:', '2')
n = int(io.recvline().split(b' = ')[-1].decode())
e = 65537
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your choice:', '1')
c = pow(2, e, n)
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your ciphertext in hex string:', hex(c))
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your magic number:', str(2 ** 69))
lo, hi = 2, 2 ** 1012
q = 0
while not q:
mid = (lo + hi) // 2
print(mid)
if n % mid == 0:
q = mid
break
c = pow(mid, e, n)
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your choice:', '1')
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your ciphertext in hex string:', hex(c))
recv = int(io.recvline().decode(), 16)
if recv == mid:
lo = mid + 1
else:
hi = mid - 1
io.sendlineafter(b'Enter your choice:', '3')
ct = int(io.recvline(), 16)
p = n // q
d = pow(65537, -1 , n - p - q + 1)
flag = pow(ct, d, n)
print(ltb(flag))
# BPCTF{How_many_queries_did_you_use?}
io.interactive()
Super Computer
Challenge
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
from Crypto.Util.number import GCD
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import random
k1 = 721919140332708275664160621428853988653441049264644517303176376909
k2 = 762740838008948738628397951381835990843814483667554565638672490531
# This challenge is free flag! If you have super computer :)
k = GCD((2024 ** k1 - 1) * (2024 ** k1 + 1), (2024 ** k2 - 1) * (2024 ** k2 + 1))
random.seed(k)
k = random.randbytes(16)
iv = b"S\x0f\xac'\xd0\x18\xfb\xe3\x92\xfdoc\x93\x7fJ\xfc"
ciphertext = b"8\x9a>&=Q\xc14\xcf\xab\xac\xbaa@\xa0s\xd4T\x18\x1f\x82\x04F\xdb\xa2\xc2\xb9V\x04\xcbG6\xe54U\x1d2\xe2q\x0b\xe6\x9b\x1e\x8d\xc6\x8c7/"
cipher = AES.new(key = k, iv = iv, mode = AES.MODE_CBC)
flag = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)
print(flag)
Mình cần tính k:
1
2
3
4
k1 = 721919140332708275664160621428853988653441049264644517303176376909
k2 = 762740838008948738628397951381835990843814483667554565638672490531
k = GCD((2024 ** k1 - 1) * (2024 ** k1 + 1), (2024 ** k2 - 1) * (2024 ** k2 + 1))
Solution
Vì k1, k2 khá lớn nên mình không tính trực tiếp được, mình sẽ tìm cách tính với số bé hơn.
Note: Mình viết $GCD(a, b)$ là $(a, b)$
Giả sử mình muốn tính $(a^m - 1, a^n - 1)$, $m = qn + r$
\[\begin{aligned} (a^m - 1, a^n - 1) &= (a^m - 1, a^m - a^n) \\ &= (a^m - 1, a^{qn}(a^{m - qn} - 1)) \\ &= (a^n - 1, a^r - 1) \\ &= \dots &\text{Tiếp tục lặp lại quá trình này đến khi r = 0}\\ &= (a^{(m, n)} - 1, 0) \\ & = a^{(m, n)} - 1 \end{aligned}\]Vậy mình chỉ cần tính $2024^{(2k_1, 2k_2)} - 1$
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
from Crypto.Util.number import GCD
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import random
k1 = 721919140332708275664160621428853988653441049264644517303176376909
k2 = 762740838008948738628397951381835990843814483667554565638672490531
# This challenge is free flag! If you have super computer :)
k = 2024 ** (2 * GCD(k1, k2)) - 1
random.seed(k)
k = random.randbytes(16)
iv = b"S\x0f\xac'\xd0\x18\xfb\xe3\x92\xfdoc\x93\x7fJ\xfc"
ciphertext = b"8\x9a>&=Q\xc14\xcf\xab\xac\xbaa@\xa0s\xd4T\x18\x1f\x82\x04F\xdb\xa2\xc2\xb9V\x04\xcbG6\xe54U\x1d2\xe2q\x0b\xe6\x9b\x1e\x8d\xc6\x8c7/"
cipher = AES.new(key = k, iv = iv, mode = AES.MODE_CBC)
flag = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)
print(flag)
# BPCTF{All_we_need_is_Euclid_algorithm}
Super Computer V2
Challenge
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import random
p = 105063592580446545974028951012743983897531876308535061339451568776273476140417
a = [83976481011811924301399130599504493293806898813567214331578547737846462043958, 49020426275786164529115108197272670769137595551571093637487791519433419519672, 24128105217328007401966909205085981217503713864081435807557452995781759742691, 54164402277699203441372828355514660347224703731247371001251599709472819892728, 5692038086237571692337343150891799220298365811757620367764289696380335050730, 9194117858273293290441837426276641586104842710061165598417982956745859622444, 27514892046750325649899981908633136074585793442699873185550644927834059630396, 66943725126331355485802310409645040036783514684318190205044041417883671830813, 36611954202140140239054776427180396851470554264500586218901125625358436893646, 93863495610885066386571402764570126016623604962463646403287688220849161122613]
b = [97461761096716147515500249810325859398244538389518130625167636466504806053237, 16186849429230042905493135221645960782811658483413984147534270789857649397900, 71342178650803093723481761619050183147490358888778566439516835390010233583079, 42978771428288111481549054267767962257445180314707234054048040896605726288851, 29120967694716870074542540604659996320145561630287811543954439503459626728291, 42698044025699644061005796009375197205179997240105171525488864698040253468486, 7809495582561305433394495659190738835412543684981410733357553129731203148539, 32385280315917393807024145684356627341683296786146343663491116566930261796667, 13004050673282999217589086204520195844228711320714522230534397332477244173876, 71584418374288378249025460600779108813126354610745231566224182660591294310622]
y = b
# This challenge is free flag! If you have super computer v2 :)
n = 2 ** 2976579765
for i in range(n):
x = sum(aa * yy for aa, yy in zip(a, y)) % p
y = [x] + y[:0:-1]
random.seed(x)
k = random.randbytes(16)
iv = b"S\x0f\xac'\xd0\x18\xfb\xe3\x92\xfdoc\x93\x7fJ\xfc"
ct = b"9\x18~C<3\xba\x04\xfb\x04t\x94\x7f\x86t\xb7\x9b\x9b\xc0N8\x0c\x8er]\x14\xfd\x033\xac;PVa\xd0m\xfdH\xf4pI\xf7s\xd5\xc2\x03\t\x9a\x1d\x96<?k\x16\xc0GVp\xcdj#\xde\xe8\x991\xb7k\xc7\xe2^\xd5h\xa7\xf8\x07\x02\xf9\xcee\xbej \x86y\xf6\xf3T\x8c8\x85\x11Ps\xb1E\xe5WK\xb3\xcbE}\xbb\xc7\x10\xea\xb92FJ\xf6\xde&I\x99\xd8\xa9\xae\x94\x0675\xcelc\x1a\xe4\x9c"
cipher = AES.new(key = k, iv = iv, mode = AES.MODE_CBC)
print(cipher.decrypt(ct))
Mình cần tính x sau vòng lặp
1
2
3
4
5
n = 2 ** 2976579765
for i in range(n):
x = sum(aa * yy for aa, yy in zip(a, y)) % p
y = [x] + y[:0:-1]
Solution
Vì các phép toán trong vòng lặp là tuyến tính nên mình có thể biểu diễn lại dưới dạng ma trận:
\[\begin{aligned} \left(\begin{array}{cc} x \\ b_9 \\ \vdots \\ b_2 \\ b_1 \end{array}\right) = \left(\begin{array}{cc} a_0 & a_1 & a_2 & \dots & a_9 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & \dots & 1 \\ \vdots &\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & \dots & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & \dots & 0 \end{array}\right) \left(\begin{array}{cc} b_0 \\ b_1 \\ \vdots \\ b_8 \\ b_9 \end{array}\right) \end{aligned}\]Vậy mình chỉ cần tính: $A^n b$ và lấy phần tử đầu tiên.
Tuy nhiên vì $n$ khá lớn nên thay vì tính $A^n$ thì mình sẽ tính $A^{m}$ với $n \equiv m \pmod {o}$. Trong đó $o$ là bậc của $A$ (tức $A^o = I$).
Chúng ta có thể tìm $o$ bằng A.multiplicative_order() trong sage
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import random as ran
from sage.all import *
p = 105063592580446545974028951012743983897531876308535061339451568776273476140417
a = [83976481011811924301399130599504493293806898813567214331578547737846462043958, 49020426275786164529115108197272670769137595551571093637487791519433419519672, 24128105217328007401966909205085981217503713864081435807557452995781759742691, 54164402277699203441372828355514660347224703731247371001251599709472819892728, 5692038086237571692337343150891799220298365811757620367764289696380335050730, 9194117858273293290441837426276641586104842710061165598417982956745859622444, 27514892046750325649899981908633136074585793442699873185550644927834059630396, 66943725126331355485802310409645040036783514684318190205044041417883671830813, 36611954202140140239054776427180396851470554264500586218901125625358436893646, 93863495610885066386571402764570126016623604962463646403287688220849161122613]
b = [97461761096716147515500249810325859398244538389518130625167636466504806053237, 16186849429230042905493135221645960782811658483413984147534270789857649397900, 71342178650803093723481761619050183147490358888778566439516835390010233583079, 42978771428288111481549054267767962257445180314707234054048040896605726288851, 29120967694716870074542540604659996320145561630287811543954439503459626728291, 42698044025699644061005796009375197205179997240105171525488864698040253468486, 7809495582561305433394495659190738835412543684981410733357553129731203148539, 32385280315917393807024145684356627341683296786146343663491116566930261796667, 13004050673282999217589086204520195844228711320714522230534397332477244173876, 71584418374288378249025460600779108813126354610745231566224182660591294310622]
y = b
A = Matrix(GF(p), a)
for i in range(len(a) - 1, 0, -1):
v = [0] * len(a)
v[i] = 1
A = A.stack(vector(v))
o = A.multiplicative_order()
# n = 2 ** 2976579765
n = pow(2, 2976579765, o)
print(n)
print(pow(2, 2976579765, p))
t = vector(GF(p), b)
An = A ** n * t
x = int(An[0])
ran.seed(x)
k = ran.randbytes(16)
iv = b"S\x0f\xac'\xd0\x18\xfb\xe3\x92\xfdoc\x93\x7fJ\xfc"
ct = b"9\x18~C<3\xba\x04\xfb\x04t\x94\x7f\x86t\xb7\x9b\x9b\xc0N8\x0c\x8er]\x14\xfd\x033\xac;PVa\xd0m\xfdH\xf4pI\xf7s\xd5\xc2\x03\t\x9a\x1d\x96<?k\x16\xc0GVp\xcdj#\xde\xe8\x991\xb7k\xc7\xe2^\xd5h\xa7\xf8\x07\x02\xf9\xcee\xbej \x86y\xf6\xf3T\x8c8\x85\x11Ps\xb1E\xe5WK\xb3\xcbE}\xbb\xc7\x10\xea\xb92FJ\xf6\xde&I\x99\xd8\xa9\xae\x94\x0675\xcelc\x1a\xe4\x9c"
cipher = AES.new(key = k, iv = iv, mode = AES.MODE_CBC)
print(cipher.decrypt(ct))
# BPCTF{Man1pula7in6_M4tr1X_l1k3_M4gic}
Hash Collision
Challenge
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
import string
import random
with open('./FLAG.txt', 'rb') as f:
flag = f.read().decode()
s = string.ascii_letters
l = 20
def check(a):
if len(a) != 20:
return True
for x in a:
if x not in s:
return True
return False
def h(msg, c, m):
res = 0
for x, y in zip(msg, c):
res += x * y
res %= m
return res
m = random.randint(2 ** 127, 2 ** 128)
c = [random.randint(2 ** 69, 2 ** 75) for i in range(l)]
print(f"m = {m}")
print(f"c = {c}")
while True:
print("Give me two strings a and b of length such that a != b and h(a, c, m) = h(b, c, m): ")
a = input()
b = input()
if check(a) or check(b):
print("Can't read that")
exit()
if a == b:
print("No")
exit()
a = a.encode()
b = b.encode()
if h(a, c, m) == h(b, c, m):
print(f"Congrats! Here's your flag: {flag}")
exit()
else:
print("Unlucky")
exit()
Đề bài yêu cầu mình nhập 2 chuỗi có 20 kí tự nằm trong chữ cái ascii (abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ). Đồng thời 2 chuỗi đó (gọi là a và b) thỏa mãn:
Với c và m cho trước.
Solution
Viết lại phương trình trên một chút, mình sẽ có:
\[\begin{aligned} &\sum^{19}_{i=0}{c_i(a_i-b_i)} \equiv 0 \pmod{m} \\ &\sum^{19}_{i=0}{c_i(a_i-b_i) = km} \\ \end{aligned}\]Vì mình cần các kí tự trong a và b đều nằm trong chữ cái ascii nên mình chỉ cần tìm các $a_i - b_i$ có giá trị bé. Mình có thể dùng LLL để làm điều này.
Xét lattice $L$ được tạo bởi basis $M$ sau đây:
\[\begin{aligned} M = \left(\begin{array}{cc} c_0 & 1 & 0 & \dots & 0 \\ c_1 & 0 & 1 & \dots & 0 \\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ c_{19} & 0 & 0 & \dots & 1 \\ m & 0 & 0 & \dots & 0 \end{array}\right) \end{aligned}\]Để ý rằng vector $(0, a_0 - b_0, \dots, a_{19} - b_{19})$ là một vector ngắn nằm trong $L$ được tạo bởi tổ hợp tuyến tính $(a_0 - b_0, a_1 - b_1, \dots, a_{19} - b_{19}, k)$.
Vậy mình tạo ra a thỏa điều kiện đề bài rồi dùng LLL để tìm $a_i - b_i$, từ đó có được b.
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import string
import random as ran
from pwn import *
LOCAL = False
if LOCAL: io = process(["python3", "server.py"])
else: io = remote('blackpinker.rocks', 30160)
m = int(io.recvline().split(b' = ')[-1].decode())
c = eval(io.recvline().split(b' = ')[-1].decode())
io.recvline()
s = string.ascii_letters
l = 20
def check(a):
if len(a) != 20:
return True
for x in a:
if x not in s:
return True
return False
def h(msg, c, m):
res = 0
for x, y in zip(msg, c):
res += x * y
res %= m
return res
t = 1
while True:
print(t)
a = ''.join(ran.choices(s, k = 20)).encode()
from sage.all import *
r = c
mat = column_matrix(ZZ, r)
mat = mat.augment(identity_matrix(l))
mat = mat.stack(vector([m] + [0] * l))
lll = mat.LLL()
for r in lll.rows():
if r[0] == 0:
b = bytes([-x + y for x, y in zip(r[1:], a)])
if all(x in s.encode() for x in b):
print(a)
print(b)
io.sendline(a.decode())
io.sendline(b.decode())
io.interactive()
exit()
t += 1
# BPCTF{Yet_another_lattice_basis_reduction_algorithm_challenge}
Circle
Challenge
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad
import hashlib
import random
flag = b'BPCTF{??????????????????????????????????}'
p = 307119639745751469235752346635781766287891925576026383455555022557456022240440834093
s = random.randint(2, p - 1)
class Point:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x % p
self.y = y % p
def __add__(self, other):
x = (self.x * other.y + self.y * other.x) % p
y = (self.y * other.y - self.x * other.x) % p
return Point(x, y)
def __mul__(self, n):
R = Point(0, 1)
P = Point(self.x, self.y)
while n > 0:
if n % 2:
R += P
P += P
n >>= 1
return R
G = Point(269706932193805755534663280853021102698237187960981530911954571811593219484562877686, 64681749570942311062995683097786979736444359061659263379460834230175114182600310869)
P = G * s
k = hashlib.sha256(long_to_bytes(s)).digest()[:16]
iv = random.randbytes(16)
cipher = AES.new(key = k, iv = iv, mode = AES.MODE_CBC)
ct = cipher.encrypt(pad(flag, 16))
print(f"P = {P.x, P.y}")
print(f"iv = {iv}")
print(f"ct = {ct}")
"""
P = (66458087392047205569134518238677614962987250315628901489579974197182257590937156372, 60031618721128621274849877211225119325796011838618857532417555895902612101315597171)
iv = b'\x84G\xd8\x9c\x8f-\xdb \r\x0c3\x07\xc2\xde\xa7\xfa'
ct = b'0\x8a\x8c><p^\x9d+\xa5\xcb%\xc2\x8c78\xd3\xe1w\xc8\xd12~SL\xe1\x1c\xadw\xdc\x9b\xd3\xfe\xba\xa5\xb04\x1b\x12D\x9fC\x9b\xcd\xf3V|\x9b'
"""
Đề bài cho mình $2$ điểm $G(x_G, y_G)$, $P(x_P, y_P)$ thỏa: $P = [s]G$ ($G$ cộng chính nó $s$ lần).
Với công thức phép cộng $2$ điểm như sau:
\[(x_1, y_1) + (x_2, y_2) = (x_1y_2 + y_1x_2, y_1y_2 - x_1x_2)\]Các phép tính này được thực hiện trong $\Z_p$ với $p$ cho trước.
Mục tiêu là tìm $s$.
Solution
Bài toán này có tên gọi là logarit rời rạc (DLP), ở đây mình làm việc trên nhóm các điểm thỏa mãn phương trình đường tròn $(x^2 + y^2 \equiv 1 \pmod{p})$. Thông thường khi mình làm những bài liên quan DLP thuộc một nhóm bất kì thì mình sẽ ráng tìm một nhóm khác đẳng cấu với nhóm cũ sao cho việc giải DLP trên nhóm mới là dễ dàng.
Một trong những điều kiện để cho bài toán DLP trở nên dễ dàng chính là smooth order (bậc của nhóm là tích các con số nguyên tố nhỏ).
Vậy đầu tiên mình đi kiểm tra xem $p - 1$ có smooth hay không.
1
2
3
sage: p = 307119639745751469235752346635781766287891925576026383455555022557456022240440834093
sage: factor(p - 1)
2^2 * 3715183 * 3759101 * 17817311 * 557030717 * 651593951 * 51289524067 * 100307721973 * 188500020953 * 876618444731
Ước nguyên tố lớn nhất của $p - 1$ chỉ cỡ $2^{40}$, vậy bậc khá smooth. Từ đây mình sẽ cố gắng tìm một ánh xạ $f$ sao cho
\[\begin{aligned} f: \Z_p \times \Z_p &\rightarrow \Z_p \\ \end{aligned}\]$f$ thỏa: $f((x_1, y_1) + (x_2, y_2)) = f(x_1, y_1) * f(x_2, y_2)$
Ở đây $*$ là một phép toán mà mình chưa biết, có thể là cộng hoặc nhân tùy vào $f$.
Chiến thuật để tìm $f$ của mình như sau:
Đầu tiên mình đi xét $(x, y) + (x, y) = (2xy, y^2 - x^2) = (a, b)$ (Theo công thức của phép cộng $2$ điểm). Mình để ý $a + b = y^2 + 2xy - x^2$ xém chút nữa là tạo ra được hằng đẳng thức.
Tuy rằng mình không biết việc tạo ra được hằng đẳng thức có giúp ích gì hay không nhưng nó cũng là 1 pattern đáng để thử. Vì bị dính $-1$ không thể tạo ra hằng đẳng thức nên mình sẽ chế ra một con $d \in \Z_p$ sao cho $d^2 = -1$ (nếu như đang làm việc trong tập số phức thì $d = i$)
Khi này mình sẽ có: $(x, y) + (x, y) = (2xy, y^2 + d^2x^2) = (a, b)$, tới đây thì nhận thấy $b + da = (dx)^2 + 2dxy + y^2 = (dx + y)^2 = (y + dx)(y+dx)$
Vậy nên mình sẽ đặt $f(x, y) = y + dx$. Dễ dàng nhận thấy nhóm các điểm trên đường tròn đẳng cấu với $\Z_p$ thông qua ánh xạ $f$:
\[\begin{aligned} f((x_1, y_1) + (x_2, y_2)) &= f(x_1y_2 + y_1x_2, y_1y_2 - x_1x_2) \\ &= (y_1y_2 - x_1x_2) + d(x_1y_2 + y_1x_2) \\ &= d^2x_1x_2 + d(x_1y_2 + y_1x_2) + y_1y_2\\ &= y_1(y_2 + dx_2) + dx_1(y_2 + dx_2) \\ &= (y_1 + dx_1)(y_2 + dx_2)\\ &= f(x_1, y_1)f(x_2, y_2) \end{aligned}\]Vậy $*$ lúc trước chính là phép nhân. Mình tiến hành giải DLP bằng Pohlig-Hellman (do bậc smooth), thuật này được cài đặt sẵn trong sage.
Script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
from sage.all import *
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import hashlib
p = 307119639745751469235752346635781766287891925576026383455555022557456022240440834093
class Point:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x % p
self.y = y % p
def __add__(self, other):
x = (self.x * other.y + self.y * other.x) % p
y = (self.y * other.y - self.x * other.x) % p
return Point(x, y)
def __mul__(self, n):
R = Point(1, 0)
P = Point(self.x, self.y)
while n > 0:
if n % 2:
R += P
P += P
n >>= 1
return R
G = Point(269706932193805755534663280853021102698237187960981530911954571811593219484562877686, 64681749570942311062995683097786979736444359061659263379460834230175114182600310869)
P = Point(66458087392047205569134518238677614962987250315628901489579974197182257590937156372, 60031618721128621274849877211225119325796011838618857532417555895902612101315597171)
iv = b'\x84G\xd8\x9c\x8f-\xdb \r\x0c3\x07\xc2\xde\xa7\xfa'
ct = b'0\x8a\x8c><p^\x9d+\xa5\xcb%\xc2\x8c78\xd3\xe1w\xc8\xd12~SL\xe1\x1c\xadw\xdc\x9b\xd3\xfe\xba\xa5\xb04\x1b\x12D\x9fC\x9b\xcd\xf3V|\x9b'
d = Zmod(p)(-1).sqrt()
def f(x, y):
return (y + d * x) % p
g = f(G.x, G.y)
a = f(P.x, P.y)
s = discrete_log(GF(p)(a), GF(p)(g), ord = p - 1)
k = hashlib.sha256(long_to_bytes(s)).digest()[:16]
cipher = AES.new(key = k, iv = iv, mode = AES.MODE_CBC)
print(cipher.decrypt(ct))
# BPCTF{Group_isomorphism_and_smooth_order}